(i) Cyanohydrin:
Cyanohydrins are organic compounds having the formula RR′C(OH)CN, where R and R′
can be alkyl or aryl groups.

Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess
sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst to field cyanohydrin. These reactions are known as
cyanohydrin reactions.
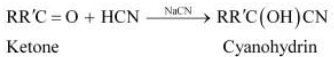
Cyanohydrins are useful synthetic intermediates.
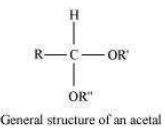
(ii) Acetal:
Acetals are gem−dialkoxy alkanes in which two alkoxy groups are present on the terminal
carbon atom. One bond is connected to an alkyl group while the other is connected to a
hydrogen atom.
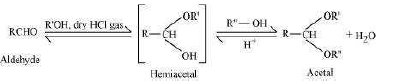
When aldehydes are treated with two equivalents of a monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas, hemiacetals are produced that further react with one more molecule of alcohol to yield acetal.
(iii) Semicarbarbazone:
Semicarbazones are derivatives of aldehydes and ketones produced by the condensation
reaction between a ketone or aldehyde and semicarbazide.
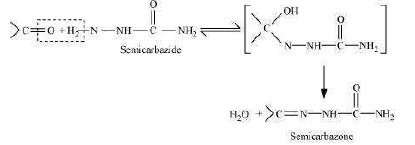
Semicarbazones are useful for identification and characterization of aldehydes and
ketones.
A β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone is known as an aldol. It is produced by the condensation
reaction of two molecules of the same or one molecule each of two different aldehydes or
ketones in the presence of a base.

(v) Hemiacetal:
Hemiacetals are α−alkoxyalcohols

(vi) Oxime:
Oximes are a class of organic compounds having the general formula RR′CNOH, where R
is an organic side chain and R′ is either hydrogen or an organic side chain. If R′ is H, thenn it is known as aldoxime and if R′ is an organic side chain, it is known as ketoxime.
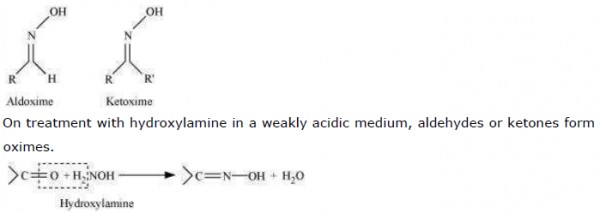
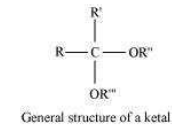
(vii) Ketal:
Ketals are gem−dialkoxyalkanes in which two alkoxy groups are present on the same
carbon atom within the chain. The other two bonds of the carbon atom are connected to
two alkyl groups.
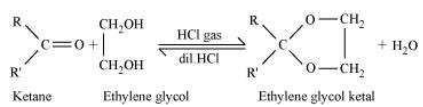
Ketones react with ethylene glycol in the presence of dry HCl gas to give a cyclic product
known as ethylene glycol ketals.
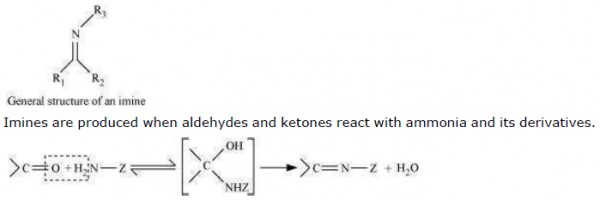
Imines are chemical compounds containing a carbon nitrogen double bond.
(ix) 2, 4−DNP−derivative:
2, 4−dinitrophenylhydragones are 2, 4−DNP−derivatives, which are produced when
aldehydes or ketones react with 2, 4−dinitrophenylhydrazine in a weakly acidic medium.
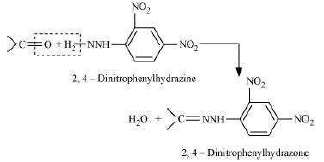
To identify and characterize aldehydes and ketones, 2, 4−DNP derivatives are used.
(x) Schiff’s base:
Schiff’s base (or azomethine) is a chemical compound containing a carbon-nitrogen double
bond with the nitrogen atom connected to an aryl or alkyl group-but not hydrogen. They
have the general formula R1R2C = NR3. Hence, it is an imine. It is named after a scientist, Hugo Schiff.
