Chapter 2
Acids, Bases, and Salts
Class X
EXERCISE SOLUTIONS
Question 1:
A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Answer 1:
(d) Bases turn red litmus blue and acids turn blue litmus red. The basic solution has a pH value of more than 7. Since the solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be 10.
Question 2:
A solution reacts with crushed eggshells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KCl
Answer 2:
(b) The solution contains HCl.
Question 3:
10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralized by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 ml of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralize it will be
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL
Answer 3:
(d) 16 mL of HCl solution will be required.
Question 4:
Which one of the following types of medicines are used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic
Answer 4:
(c) Antacid is used for treating indigestion.
Question 5:
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when −
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminum powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Answer 5:
(a) Sulphuric acid + Zinc → Zinc sulfate + Hydrogen
H2SO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
(b) Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
2HCl(aq) + Mg(s) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(c) Sulphuric acid + Aluminium → Aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen
3H2SO4(aq) + 2Al(s) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g)
(d) Hydrochloric acid + Iron → Ferric chloride + Hydrogen
6HCl(aq) + 2Fe(s) → 2FeCl3(aq) + 3H2(g)
Question 6:
Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorized as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Answer 6:
Two nails are fitted on a cork and are kept in a 100 mL beaker. The nails are then connected to the two terminals of a 6-volt battery through a bulb and a switch. Some dilute HCl is poured into the beaker and the current is switched on. The same experiment is then performed with glucose solution and alcohol solution.
Observations: It will be observed that the bulb glows in the HCl solution and does not glow in the glucose solution.
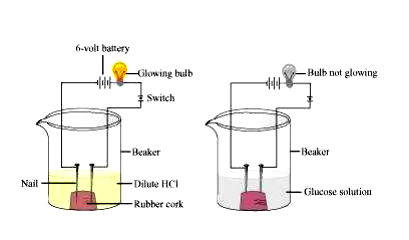
Result: HCl dissociates into H+ and Cl− ions. These ions conduct electricity in the solution resulting in the glowing of the bulb. On the other hand, the glucose solution does not dissociate into ions. Therefore, it does not conduct electricity.
Conclusion: From this activity, it can be concluded that all acids contain hydrogen but not all compounds containing hydrogen are acids. That is why, though alcohols and glucose contain hydrogen, they are not categorised as acids.
Question 7:
Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Answer 7:
Distilled water is a pure form of water and is devoid of any ionic species. Therefore, it does not conduct electricity. Rainwater, being an impure form of water, contains many ionic species such as acids and therefore it conducts electricity.
Question 8:
Why do acids not show acidic behavior in the absence of water?
Answer 8:
Acids do not show acidic behavior in the absence of water because the dissociation of hydrogen ions from an acid occurs in the presence of water only. It is the hydrogen ions that are responsible for the acidic behavior.
Question 9:
Five solutions A, B, C, D, and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7, and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) neutral?
(b) strongly alkaline?
(c) strongly acidic?
(d) weakly acidic?
(e) weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
Answer 9:
(a) Neutral → Solution D with pH 7
(b) Strongly alkaline → Solution C with pH 11
(c) Strongly acidic → Solution B with pH 1
(d) Weakly acidic → Solution A with pH 4
(e) Weakly alkaline → Solution E with pH 9
The pH can be arranged in the increasing order of the concentration of hydrogen ions as: 11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1
Question 10:
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer 10:
The fizzing will occur strongly in test tube A, in which hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added. This is because HCl is a stronger acid than CH3COOH and therefore produces hydrogen gas at a faster speed due to which fizzing occurs.
Question 11:
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer 11:
The pH of milk is 6. As it changes to curd, the pH will reduce because curd is acidic in nature. The acids present in it decrease the pH.
Question 12:
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer 12:
(a) The milkman shifts the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline because, in alkaline conditions, milk does not set as curd easily.
(b) Since this milk is slightly more basic than usual milk, acids produced to set the curd are neutralized by the base. Therefore, it takes a longer time for the curd to set.
Question 13:
Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Answer 13:
Plaster of Paris (POP) should be stored in a moisture-proof container because Plaster of Paris, a powdery mass, absorbs water (moisture) to form a hard solid known as gypsum.
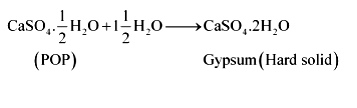
Question 14:
What is a neutralization reaction? Give two examples.
Answer 14:
A reaction in which an acid and base react with each other to give salt and water is termed a neutralization reaction. In this reaction, energy is evolved in the form of heat.
For example:
- NaOH (Base) + HCl (Acid) → NaCl (Salt) + H2O (Water)
- During indigestion (caused due to the production of excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach), we administer an antacid (generally milk of magnesia, Mg(OH)2 which is basic in nature). The antacid neutralizes the excess of acids and thus gives relief from indigestion.
Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl → MgCl2 +2H2O
Question 15:
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer 15:
Two important uses of washing soda and baking soda are as follows:
(1) Washing soda:
(a) It is used in glass, soap, and paper industries.
(b) It is used to remove the permanent hardness of the water.
(2) Baking soda:
(a) It is used as baking powder. Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and a mild acid known as tartaric acid. When it is heated or mixed in water, it releases CO2 that makes bread or cake fluffy.
(b) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.