(4) (+15°) and (11.3 m/s) \(\hat{j}\)
The initial horizontal (or x) and vertical (or y) component, of the velocity of the ball, are v cos 45° and v sin 450 respectively.
The surface being smooth, the final (i.e. after ‘reflection’) horizontal component, of the velocity of the ball, would still be v cos 45° . The vertical component, however, would be (e v sin 45° ). The vertical component, however, would be (e v sin 45°). If therefore, the final velocity (v) of the ball makes an angle θ with the horizontal, we have

The angle of ‘reflection’ is, therefore, (90°–30° ) = 60° . Hence the diference, between the angle of ‘reflection’ and the angle of incidence, is (60°–45° ) = +15° .
The final velocity, V is given by
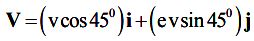
The initial velocity, V, is given by

∴ Change in velocity
