The changes in concentration of the reactants or products are experimentally determined by withdrawing a small portion of the reaction mixture (usually 2 or 5 ml) at suitable intervals of time and then freeze to about 0°C to stop the reaction. The concentration of the reactant or product is measured by a suitable method. A plot of concentration-time is made from the graph, the average rate, instantaneous and initial rates can be determined.
(i) Average rate
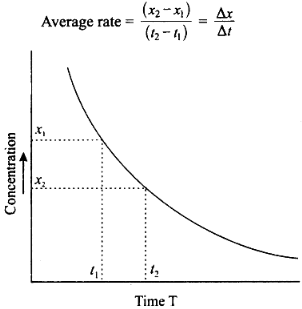
Two equivalent points are taken with respect to the time at which the average rate is to be determined. The concentrations corresponding to these points are noted from the graph. The difference in concentration is divided by the time interval between equidistant points. Two equidistant points with respect to T is selected. Let these be ‘t1,’ and ‘t2’ respectively. The corresponding concentrations are x1, and x2 respectively.
(ii) Instantaneous rate of reaction:
For the determination of the instantaneous rate of reaction at any time ‘t’, a tangent is the direction to the curve at the point ‘P’ corresponding to that time. The slope of this tangent gives the instantaneous rate of reaction.

Where Q is the angle of a tangent with the time axis. In a similar manner, the rate of formation of the product can be determined by measuring the slope of the tangent at a particular instant in concentration to the time curve.
(iii) Initial rate of reaction:

The rate of reaction is maximum at the time of mixing the concentration. This cannot be determined experimentally. This is determined from the concentration is time curve. The curve is extrapolated to zero time and the slope of this curve at zero time gives the initial rate of the reaction.
\(\frac {\Delta x}{\Delta t}\) = initial rate.