Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. The sides of this triangle have been named Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse.
Pythagoras Theorem Proof
Given: A right-angled triangle ABC, right-angled at B.
To Prove: AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Construction: Draw a perpendicular BD meeting AC at D.
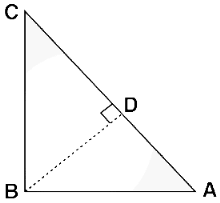
Proof:
We know, △ADB ~ △ABC
Therefore,
\(\frac{AD}{AB} = \frac{AB}{AC}\)
(corresponding sides of similar triangles)
Or, AB2 = AD × AC ………(1)
Also, △BDC ~ △ABC
Therefore,
\(\frac{CD}{BC} = \frac{BC}{AC}\)
(corresponding sides of similar triangles)
Or, BC2 = CD × AC ……..(2)
Adding the equations (1) and (2) we get,
AB2 + BC2 = AD × AC + CD × AC
AB2 + BC2 = AC (AD + CD)
Since, AD + CD = AC
Therefore, AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Hence, the Pythagorean theorem is proved.