Correct option is (B) onto
f : R+ → [−5, ∞] given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5
To show: f is one-one & onto
Let us assume that f is not one-one.
\(\therefore\) there exists 2 as more numbers for which images are same
For x1, x2 ∈ R + & x1 ± x2
Let f(x1) = f(x2)
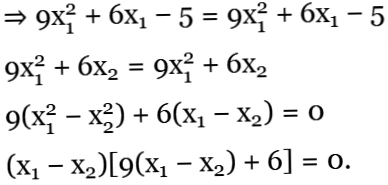
Since x1 & x2 are positive
9(x1 − x2) + 6 > 0
\(\therefore\) x1 − x2 = 0 ⇒ x1 = x2
Therefore, it contradicts are assumption.
Hence the function is one-one
Now, let as prove that f is onto
A function f : X → Y is onto it for every y ∈ Y, these exists a pie image in X.
f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5
= 9x2 + 6x + 1 −6
= (3x + 1)2 − 6
Now, for all x ∈ R + as [0, ∞), f(x) ∈ [−5 ,∞)
\(\therefore\) Range = co-domain
Hence f is onto
We have proved, that function is one-one & onto. Hence in turn it is proved that f is invertible.