(A) Internal structure of a dicot stem:
(i) Epidermis: It is the outermost single layered covering of stem having no intercellular spaces. It is covered by cuticle to reduce transpiration. Multicellular hairs are also present.
(ii) Cortex: Inner to the epidermis is cortex consisting of multilayered hypodermis and parenchymatous cortex to provide mechanical strength. Resin ducts may be in the region of cortex.
(iii) Endodermis: It is the outermost layer of cortex having barrel-shaped parenchyma cells containing starch grains.
(iv) Stele: Stele includes Pericycle, vascular bundles, pith (medulla) and pith rays (medullary rays).
Vascular bundles vary from 5-7 in numbers and are arranged in a ring. They are open and collateral.
Xylem is endarch. Pith lies in the centre having parenchyma cells with intercellular spaces.

Fig. T.S of Dicot stem
(B) Internal structure of a dicotyledonous root:
(i) Epiblema: It is called piliferous layer (outermost one-celled thick). Unicellular root hairs extend to outside from the epiblema.
(ii) Cortex: It is the main part of root having many layers of rounded parenchymatous cells containing starch grains. Intercellular spaces are present in between them. It stores food substances.
(iii) Endodermis: It lies inner to cortex and contains barrel-shaped cells having no intercellular spaces. Radial walls of its cells may have lignified casparian strips. Water and minerals pass through passage cells to phloem.
(iv) Stele: It is the central part of dicot root. Inner to endodermis lies Pericycle which is single layered thick only. Vascular bundles form a ring. Phloem and xylem are present in different radii to form separate bundles.
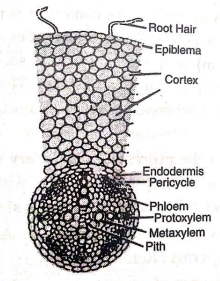
Fig. T.S of a portion of dicot root
Xylem in exarch: In the centre, pith and xylem fuse together. Phloem has sieve tubes, companion cells and phloem parenchyma. Between xylem and phloem conjunctive tissue is present.